Energy Efficiency, Solar Energy, Solar Energy Basics, Solar Financing

Many people find themselves wondering, “How many solar panels do I need to power my house?”. In this era of increasing environmental awareness and escalating energy expenses, a growing number of homeowners are seeking the same information. Nevertheless, the answer is not as simple as it may appear.
First, let’s understand what this journey involves. As you embark on this venture towards greener energy, you’ll probably navigate through various terms and concepts. Solar panels, kilowatt-hours, energy efficiency, and net metering are just a few among them. But don’t worry; that’s what we’re here for. Consider this your guide to decoding solar panel numbers.
The transition to solar energy doesn’t have to be complicated or overwhelming. With the right tools and guidance, you can easily determine the number of solar panels your home needs, paving the way towards a greener, more sustainable future.
Let’s take a walk through the basics of solar energy, to lay a firm foundation for our discussion on powering your household with solar panels. Simply put, solar energy is light and heat sourced from the sun which is converted and used to power homes efficiently and sustainably.
Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, are devices engineered to convert sunlight directly into electricity. Typically mounted on the house roof or positioned on the ground within the property to optimize sun exposure, these panels play a crucial role in harnessing solar energy.
At the heart of each solar panel are solar cells, which are the working units responsible for the magic of turning sunlight into electric power. These cells are crafted from a semiconductor material, usually silicon, and they spring into action, generating electric current as sunlight hits them. However, the current produced is direct current (DC), which needs to be converted into alternating current (AC) to power household appliances. This critical conversion is carried out by a component known as the inverter, making it an indispensable part of the solar power equation.
How Solar Energy Works: To make electricity from sunlight, solar panels capture photons from sunlight, initiating an electric current. The inverter then transforms this DC into AC electricity. Your house consumes this power, and any excess electricity gets fed back into the power grid.
Now, with a basic understanding of solar energy and how it works to power houses, we will discuss how many solar panels are needed to power a typical household.

Transitioning to solar energy is an exciting decision with multiple factors requiring careful consideration. One critical aspect is determining how many solar panels your home requires, and in this guide, we break it down for you.
Eyeing the U.S. average, it would take around 15 to 19 panels to offset a monthly electricity bill of $140.
The quantity of solar panels required to cater to your house’s power needs is influenced by various factors. These considerations may include your house’s location, energy consumption, and the sizing of the solar panels.
Imagine being able to power your entire home with inexhaustible solar energy! For the typical American household, harnessing the sun’s energy could mean having between 15 and 19 solar panels. This figure is based on the national average electricity use of about 893 kilowatt-hours (kWh) each month. The investment for buying and installing such a number of solar panels generally falls in the range of $12,000 and $17,000 – that’s after factoring in your savings from the federal solar tax credit.
But let’s hit the pause button right there; your house isn’t ‘average’, and neither are you! It’s quite possible that your energy consumption patterns don’t precisely match the national average. Moreover, determining the right amount of solar paneling for your house depends on a host of other intricate factors.
The first step towards understanding how many solar panels you’d need to power your house, is understanding your energy consumption. To calculate this, you should know about your power usage. This is often measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Power usage, simply put, refers to the amount of power an appliance uses per hour. Your consumption would then be the total amount of kWh you use over a given period. For instance, if you have an appliance rated 1000 watts (or 1 kilowatt), and it was kept on for one hour, it would consume 1 kWh of energy.
To estimate your power usage, begin by making a list of all the appliances in your household, along with their power rating (often indicated on the appliance itself) and your estimated daily use in hours. Multiple the power rating by usage hours to get daily kWh consumption by each appliance.
Note: The power rating is usually in watts. To convert it to kilowatts, divide the watt value by 1000.
Once you’ve determined the consumption for each appliance, add up all the values to determine your total daily use. To estimate your annual consumption, multiply your daily consumption by 365.
| Appliance | Power Rating (kW) | Hours Used Per Day | Daily Consumption (kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Example: Refrigerator | 0.1 kW | 24 | 2.4 kWh |
Remember, these are just estimates to give you an idea of your typical consumption. Factors like seasonal variation, improvements in energy efficiency, and changing lifestyle patterns can influence these values. Nonetheless, this basic understanding can be a good starting point when considering how many solar panels you might need for your home.
As the primary source of energy for solar panels is sunlight, the first factor to consider is the number of available sunlight hours your location receives. This will significantly influence the number of solar panels required to power your house.
In broad terms, the average number of sunlight hours a location receives can be calculated by examining the latitude and climate. Typically, areas near the equator receive more sunlight hours due to their geographical position. However, local weather patterns also play a significant role. For instance, a location with a sunny climate will naturally receive more sunlight hours than a predominantly cloudy or rainy one.
Distinct seasonal variations also impact the number of sunlight hours. In winter, the sun shines for fewer hours, leading to a drop in power generation. Thus, solar systems are usually designed to overproduce during summer to compensate for the shorter, darker winter days. Keep in mind that solar panels do not require direct sunlight to produce electricity—they can still generate power under cloudy conditions, although the efficiency can drop by about 10-25% depending on the cloud cover.
Did you know that the U.S. enjoys an average of 4.2 peak sun hours daily? That’s roughly 128 sun-kissed hours every month! However, the amount of sunlight you soak up can differ significantly depending on your location. Take Arizona, a sun lover’s paradise with over seven daily peak sun hours, compared to Alaska, which receives just two peak sun hours on average.
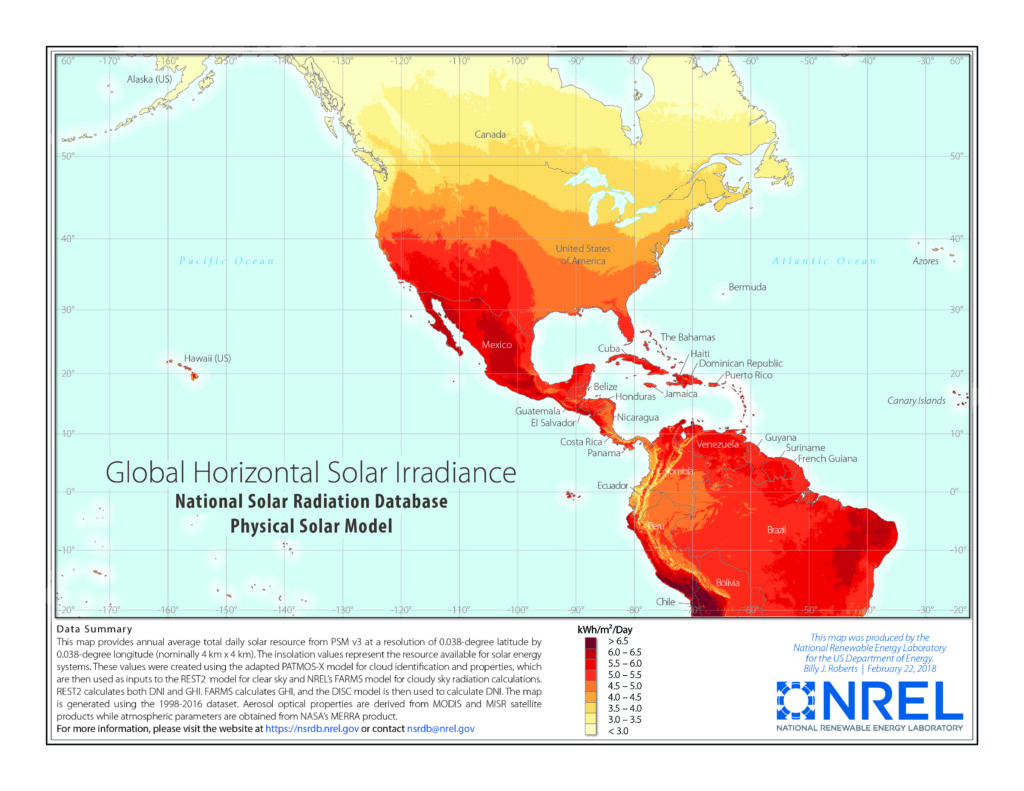
Here’s an interesting fact: the more sunlight your home basks in, the fewer solar panels you’ll require to offset your energy bills. To help visualize, let’s examine the estimated average peak sun hours across various U.S. regions:
The relationship between sunlight hours and solar panel efficiency is straightforward: the more sunlight a solar panel receives, the more power it will generate. Therefore, understanding the sunlight hours in your area is vital for proper planning and efficiency of your solar energy system.
One important factor to consider when installing solar panels is the orientation and tilt of your roof. It’s essential because it can significantly impact the amount of sunlight your solar panels receive, thus affecting their performance and, ultimately, your energy savings.
Orientation: In the United States, south-facing roofs are typically the most advantageous for solar panel installation. This is due to their exposure to the sun for the longest part of the day. East or west-facing roofs can also be suitable, though they may produce slightly less energy.
Tilt: The angle at which your solar panels are positioned is also crucial. Ideally, your tilt should be equal to your latitude, but a tilt between 30 to 45 degrees can also be effective for most U.S locations.
The orientation and tilt of your rooftop play a critical role in the efficiency of your solar power system. Engaging a professional installer can help optimize these factors for your unique location.

Embarking on the path to a solar-powered household offers a liberating chance to break away from municipal grids. Realizing this dream, however, greatly depends on your understanding of Net Metering and Battery Storage. These two integral parts of a solar energy system not only bolster its efficiency but also affect the number of solar panels your home might need.
Net Metering: Net Metering is a system that credits you for excess electricity generated by your solar energy systems, which is then fed back into the grid. The more energy your solar panels produce beyond your consumption, the more credit you receive on your utility bill. Net metering helps reduce the number of solar panels needed in a household. It operates on a zero-waste principle, ensuring all energy generated is utilized. Surplus energy produced beyond household consumption is returned to the grid, making your solar energy setup more efficient. The extra energy fed back into the grid also provides financial benefits. It gives you monetary credit, which can be used when energy is needed from the grid. This method reduces the strain on your solar panels, ruling out the need for adding panels to meet extra power requirements. Net metering makes solar energy a cost-effective choice.
Battery Storage: In the world of solar energy, battery storage is like your personal power vault, making sure the energy harvested on sunny days doesn’t disappear. Instead, it gets stored for use during night-time, power outages or those cloudy days when panel productivity dips. The impact of battery storage on the quantity of solar panels required is multifaceted. A competent battery storage system is capable of retaining excess power generated during peak solar hours for later use, which in turn reduces dependence on the grid and obviates the need for additional solar panels. While the initial investment in battery storage systems might be on the higher side, they prove to be cost-effective over time. By providing a degree of energy autonomy and contributing to reduced utility expenses, they potentially limit the size of your solar setup, making the entire solar installation more economically efficient in the long run.
Understanding net metering and battery storage is vital in determining the number of solar panels you need. By harnessing these systems effectively, you can fine-tune your solar power setup for optimum efficiency and cost-effectiveness. It’s one more step towards achieving a sustainable, eco-friendly lifestyle fueled by green energy.
One of the vital steps in solar power adoption for your home is choosing a reputable solar panel installer. This choice can dictate the success of your solar energy investment. Below are key factors you should consider when making this decision:
Relevant Experience: Experience is crucial in the solar industry. Look for companies that have been in operation for a few years and have a record of installations in your area. This assures you they are not only aware of best practices but also understand local regulations and issues.
Certifications: Ensure that the company you’re considering has relevant certifications. These certifications demonstrate that the installer has achieved a certain standard and competency in solar installation. North American Board of Certified Energy Practitioners (NABCEP) is one such certification you should look out for.
Reviews and Testimonials: Positive reviews and testimonials can give you a sense of the installer’s reputation. Look out for consistent themes in reviews, such as excellent customer service, high-quality installation, or post-installation support.
Warranty: A reliable solar installer should provide a solid warranty. High-quality solar panels typically come with 25-year warranties. Make sure your installer stands behind their work too.
Remember, a well-installed solar panel system can drastically reduce your electricity costs and contribute to a healthier environment. It’s an investment worth getting right from the beginning. Once you’ve narrowed down potential installers, request detailed quotes from each. A good solar installation quote should detail all costs upfront, including any potential additional costs for panel upgrades, roof repairs or maintenance.
The initial investment in solar panels, which includes the cost of panels, inverters, and installation, can be substantial, often ranging from $15,000 to $25,000. However, with federal incentives like the Investment Tax Credit (ITC), which offers a 26% tax credit, the upfront costs can be significantly offset. Over time, solar panels drastically cut down electricity bills, with an average saving of about $1,400 annually.
Compared to traditional electricity, where the average annual cost is about $1,500, the savings are substantial. Moreover, with net metering, homeowners can earn credits for excess energy generated, further reducing energy costs. Over the long term, solar panels not only pay for themselves but also provide a cost-effective solution to energy needs. Additionally, solar installations can increase property value by up to 4.1%, making it a sound investment for homeowners. Therefore, despite the initial costs, the long-term financial and environmental benefits make solar panels a worthy investment.

Switching to solar energy brings considerable environmental benefits, playing a vital role in our fight against climate change and various environmental problems.
💡 Every kilowatt-hour (kWh) of solar energy can offset around 0.08 pounds of nitrogen oxides, 0.3 pounds of sulfur dioxide, and 0.07 pounds of particulate matter that traditional fossil fuels would release into our atmosphere.
Let’s examine in more detail some of the environmental benefits:
Reduction in Air Pollution: Unlike traditional energy sources, solar power doesn’t release harmful pollutants. Conventional energy production emits pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, particulate matter, and nitrogen oxides that pose a threat to public health. Switching to solar power reduces this emission, leading to more breathable air quality.
Decreased Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Solar panels emit much fewer greenhouse gases in operation compared to fossil fuels. By using solar power, we can significantly reduce harmful carbon dioxide and methane emissions which are the primary contributors to global warming.
Conservation of Water Resources: Traditional electricity generation can consume billions of gallons of water each year. In contrast, solar panels require no water to generate electricity, preserving valuable water resources.
Reduction in Energy Reliance: By harvesting power directly from the sun, homes become less reliant on traditional energy grids, promoting sustainable and self-sufficient living.
With these benefits at hand, it becomes clear that embracing solar energy is not just about cost savings; it’s about creating a healthier and more sustainable planet for future generations. Let’s join the solar revolution for a greener future!
Stay a while and read more posts like this
Energy Efficiency, Green Living
Imagine reducing your home energy consumption by half. Picture your energy bill dropping significantly every month. It’s not a pipe dream in 2023....
In recent years, Europe has witnessed a remarkable surge in the adoption of solar panels, marking a pivotal shift towards renewable energy. Data from the...
Renewable Energy, Solar Energy, Solar Energy Basics, Solar Technology
“Unlock the Truth: Get the Facts on Solar Energy!” Introduction Solar energy is becoming increasingly popular as a renewable energy source, but there are...