In our goal to champion renewable energy, harness the power of the sun, and cultivate a sustainable future, we often encounter a crossroad: solar thermal or photovoltaic solar? Both technologies tap into the boundless solar energy, yet each follows a unique trajectory to convert sunlight into usable power. Solar thermal systems focus on harnessing the sun’s warmth, while photovoltaic solar systems transform sunlight into electricity. But which one is a better fit for your needs? How do they operate, and how do their efficiencies and applications differ? Let’s delve into the solar thermal vs photovoltaic debate, exploring the mechanics of these two solar power giants, comparing their efficiencies, and guiding you through their best-case applications.
Solar Photovoltaic (PV) technology falls under the umbrella of solar energy systems, standing out with its ability to directly convert sunlight into electricity. This conversion process is made possible thanks to the heart of the system: photovoltaic cells or solar cells, which are nested in the solar panels. These cells leverage a fascinating phenomenon known as the photovoltaic effect, which involves transforming light photons into voltage, or in layman’s terms, electricity.
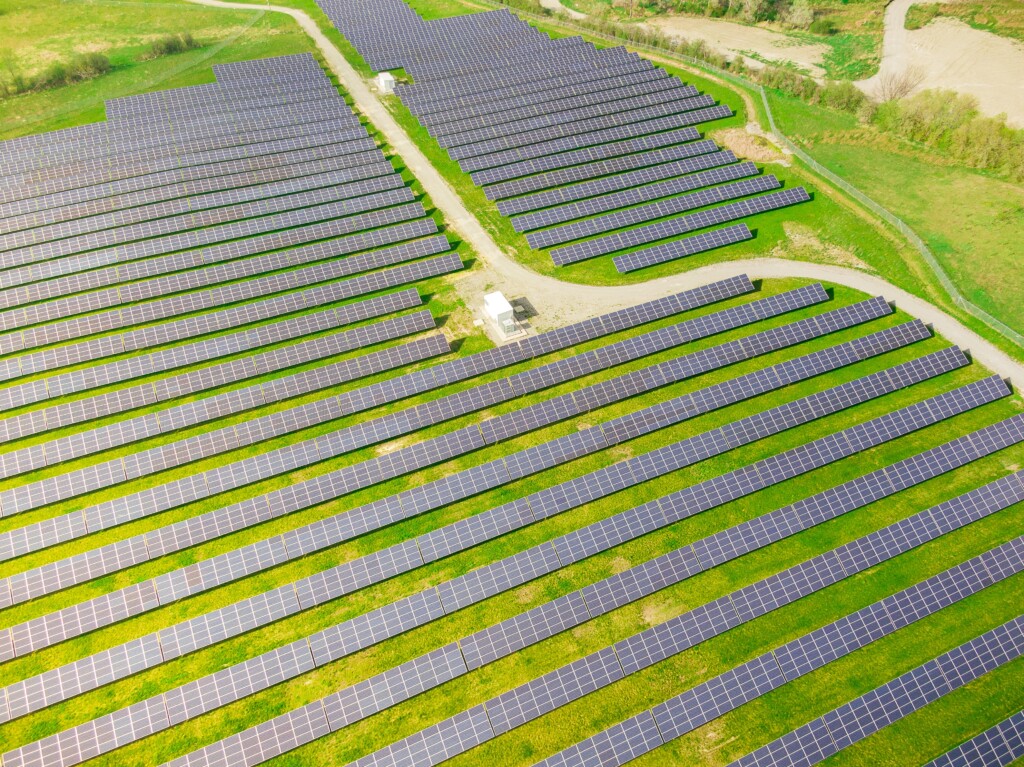

The charm of Solar PV systems lies in their versatility and applicability across numerous sectors. For instance, they’re an increasingly popular option for residential use due to their capacity to cater to regular domestic needs—from lighting to heating and cooling, down to powering the assortment of electrical appliances. Businesses, too, are drawn to PV systems as they strive to shrink their carbon footprints and trim down energy expenses. On a larger scale, solar power plants employ vast arrays of PV installations to generate electricity on a massive scale.
So how does this sunlight-to-electricity conversion happen, and what are the components that facilitate it? At the core of photovoltaic panels, you’ll find semiconductor materials—most commonly, silicon. When sunlight strikes the surface of a PV panel, energy from the photons is absorbed by the semiconductor. This absorption releases electrons from their atomic bonds, leading to a flow of electrons that results in an electric current. But there’s a catch—the electricity generated is initially a direct current (DC), which needs to be transmuted into an alternating current (AC) to be compatible with most household appliances and the electrical grid. This transformation is achieved through an invaluable device known as an inverter. Let’s elaborate more on the key components of a typical solar PV system:
Pros of Solar PV systems include their ability to provide whole-home power, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and lower electricity bills. However, they come with a high upfront cost, aesthetic concerns for some property owners, and significant space requirements. Let’s look at them in more detail.
Unlike photovoltaic systems, solar thermal systems convert sunlight into thermal energy or heat. These systems utilize thermal panels that absorb the sun’s thermal energy and transmit it to a heat-transfer fluid. This hot fluid can then be used to heat water or air. Solar thermal technology is especially beneficial for businesses and industries that require a significant amount of heat energy, such as those involved in manufacturing, food processing, or hospitality. It can also be used in residential settings, it’s particularly beneficial for the production of domestic hot water, and some systems are also used to provide space heating in the colder months. The functionality depends on the type of circulation system used, with natural circulation systems usually dedicated to hot water production and forced circulation systems also supporting space heating.
There are various types of solar thermal systems, with each type serving a different purpose. Regardless of the type, each solar thermal system works by absorbing solar energy via a heat-transfer fluid. The heated fluid is then used directly for space heating or to produce steam for mechanical energy. The primary components of a solar thermal system include:
Solar thermal systems are highly efficient, use renewable energy, and can significantly reduce heating bills. However, their uses are limited compared to solar PV systems, they may be impractical to retrofit in some homes, and their performance can be affected by changes in weather, season, or time of day.
The efficiency of a system is typically gauged by how well it can convert incoming energy. A solar thermal system, despite occupying only 3–4m² of roof area, is quite efficient. This is due to its ability to convert approximately 90% of solar radiation into heat energy. Contrastingly, a solar photovoltaic (PV) system, even though it may need up to 10m² of roof area, typically has an efficiency of around 15% to 20%. This efficiency rate, however, has been on a steady upward trajectory as the technology of solar panels progresses. It’s also important to mention that while the solar PV system’s space is mainly consumed by solar cells, a solar thermal system’s use of space extends to the indoors for water heating.
Despite its high efficiency, particularly in water heating, a solar thermal system is not without its challenges. Given its complex design that involves capturing light, converting it to energy, and using it to heat air or water, the system has more components and hence more potential for issues and maintenance costs. On the other hand, a PV System, while producing energy for a broader range of uses, is simpler and requires less maintenance.
The concept of capacity in this context refers to the maximum amount of energy a solar system can generate under optimal conditions. This is usually measured in watts (W) or megawatts (MW) — with 1 megawatt being equivalent to 1,000,000 watts. This maximum energy output is also known as the ‘rated’ or ‘nameplate’ capacity. In the case of solar thermal and photovoltaic systems, we typically see that photovoltaic systems have a higher capacity than their solar thermal counterparts. For instance, the largest photovoltaic power stations can generate over 500 megawatts of electricity under ideal conditions. On the other hand, the capacity of thermal power stations usually tops out around 400 megawatts. What this indicates is that, when considering the highest possible energy output, photovoltaic systems generally outperform solar thermal systems.
When deciding whether to opt for a solar thermal or a photovoltaic system, it is essential to first consider the type of energy required. If you need electricity, a PV system would be the optimal choice. However, if heat energy is what you need, a solar thermal system would be better suited. Let’s suppose you require both heat and electrical energy. In such a case, given the advancements in technology, the PV system would be a more suitable option. This is because electrical energy can be readily converted into other forms of energy. Over the years, solar systems have been getting increasingly efficient, and the cost of PV modules has fallen by 80% since 2009. Although solar thermal systems are more efficient and cheaper, PV systems have a larger output capacity, making them the better option in scenarios where higher power output is desired. If your primary energy requirement is for heating purposes, such as hot water for personal use or space heating, then a solar thermal system might be the more efficient choice. These systems excel in tasks related to heating, making them particularly suitable for those living in colder climates or in areas where hot water demand is high.
In summary, the choice between solar thermal and solar PV will mostly depend on the specific requirements and circumstances. It’s always a good idea to consider all factors, including cost, efficiency, capacity, and maintenance requirements, before making a decision.
The potential savings from both solar thermal and photovoltaic systems are significant and multi-faceted. They range from reducing your monthly energy bills to contributing to environmental conservation.
Let’s begin with solar thermal systems. These systems are particularly effective at reducing heating costs, which often comprise a significant portion of household expenses. On average, a solar thermal system can supply up to 60% of your hot water needs over a year, with potential for even greater efficiency during the summer months. There are also opportunities to increase these savings by adopting more energy-efficient habits. According to Green Match, solar thermal panels will save you approximately 10% on your energy expenses, with savings increasing over time as energy prices rise. The upfront costs of solar thermal systems can vary, typically ranging between $3000 and $6000. However, the overall cost can be offset through solar energy incentives. Furthermore, these systems have a long lifespan, often up to 25 years. This longevity, combined with the steadily increasing costs of traditional energy sources, suggests that you could see even larger savings in the future.
As for solar photovoltaic systems, their savings potential lies in their ability to produce electricity for a wide range of uses, from lighting to running appliances. They offer a more comprehensive approach to energy generation that can significantly reduce or even eliminate your dependence on the grid, leading to substantial savings on your electricity bill. The initial cost of a solar photovoltaic system can vary greatly depending on the size and complexity of the setup. According to Energy Sage, the average initial cost of installing solar panels in the US is $20,650, taking an average of 8.7 years to recoup the investment. However, this cost does not include the many solar energy incentives that will help you offset these costs. Like solar thermal systems, solar photovoltaic systems have a long lifespan—often up to 25 years or more—which means you can continue to reap the benefits long after the system has paid for itself.
It’s also worth noting the environmental savings associated with both systems. By harnessing renewable solar energy, you’re reducing your reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing your carbon footprint, making these systems a financially and environmentally conscious choice.
In conclusion, both solar photovoltaic and solar thermal systems present distinct advantages, each suited to specific energy needs and scenarios. The choice between the two is largely driven by your personal energy requirements and the climate in your location. If your primary energy requirement is heating, for instance, domestic hot water and space heating, a solar thermal system can be a highly efficient solution. This is especially true if you live in an area that enjoys substantial direct sunlight for much of the year. On the other hand, if your energy needs are more extensive and encompass a wide range of uses, including lighting and running appliances, a solar photovoltaic system could be the better choice. Providing a comprehensive approach to energy generation, these systems can significantly reduce your dependence on grid electricity.
Both systems represent a long-term investment that can lead to considerable cost savings over their lifecycle, often exceeding 20 years. While the initial setup cost may seem substantial, various financial incentives can help mitigate this. Moreover, the savings generated over their lifetime often make them a cost-effective solution in the long run. Ultimately, by opting for either solar thermal or solar photovoltaic technology, we make a significant contribution to environmental sustainability.
Solar thermal systems convert sunlight into heat, while photovoltaic systems convert sunlight directly into electricity.
Both systems can contribute significantly to energy independence, but photovoltaic systems offer a more comprehensive approach to energy generation as solar thermal can only provide hot water and heating.
Stay a while and read more posts like this
In recent years, Europe has witnessed a remarkable surge in the adoption of solar panels, marking a pivotal shift towards renewable energy. Data from the...
Renewable Energy, Solar Energy, Solar Energy Basics, Solar Technology
“Unlock the Truth: Get the Facts on Solar Energy!” Introduction Solar energy is becoming increasingly popular as a renewable energy source, but there are...
Imagine a world where you’re able to cut your monthly energy expenditure substantially. A reality where your home isn’t reliant on finite,...